Material Cronidur30ISO Standard: DIN 1.4108Chemical formula: X30CrMoN15-1Advantages: Finer structure, less heat generated, higher permissible contact pressure, much higher fatigue life reliability (10x compared with GCr15 in best case), better corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance Material Ceramic Si3N4Advantages: Excellent tribological properties, lower density to improve the bearing kinematics, lower coefficient of thermal expansion, no magnetism, high current insulation
A GROWING NUMBER OF “BARGAIN” BEARINGS&犀利士 nbsp;are being brought into the Heavy Duty Truck and Trailer marketplace by bearing brokers whose primary emphasis is on price. They ignore the critical issues of product integrity, performance, and supplier support. Initially the price has some attraction, but testing performed by Hyatt and other major suppliers has proven that a much superior performance is achieved from a quality product provided by a reputable manufacturer. For tapered roller bearings to achieve their Maximum Life in application (L10 Life), the load must be evenly distributed over the length of the rollers. To ensure proper distribution of bearing loads, Hyatt Tapered Roller Bearings are manufactured with a crown on the raceways and rollers. In our experience, the “bargain” products rarely have raceways and rollers that are crowned. Frequently the components have concave contact areas, generating even higher stresses within the bearing and promoting early catastrophic failure. Bearing brokers will state that their products conform to American Bearing Manufacturers Association (ABMA) specifications. These standards, however, only relate to the external dimensions of the bearing and its compatibility with the wheel hub and spindle. If you want a quality product which is going to provide years of uninterrupted service,…
Wheel hub problems are often discovered while ruling out other sources for the squealing and grinding sounds coming from that area of the vehicle or the gradually increasing vibration noticed by the driver. Because such symptoms – odd noises, vibration, deterioration in handling, etc. – The common to a variety of suspension and steering system parts, it is often through the process of elimination that the need to replace this part is apparent. the it is determined for sure that this is the source of the vehicle’s problems, however, the repair Should be made as soon as possible in order to avoid causing damage to other parts or a dangerous road situation. Those that are fairly skilled at performing automotive repair projects at home are likely to find the replacement of the hub and related parts more time consuming than Challenge. Any repair is more likely to last longer when made with quality parts,Timken, Pronto, Quality-Built, WJB, Replacement, Centric, Moog, Dorman, Genuine, Beck Arnley, First Equipment Quality, DuraGo, API, NSK and Febi. (MAPC Bearings OEM for most of these brands) Wheel Hub Assembly – Time for replacement? Wheel Hub AssemblyA hub assembly, also known as a wheel hub assembly or…
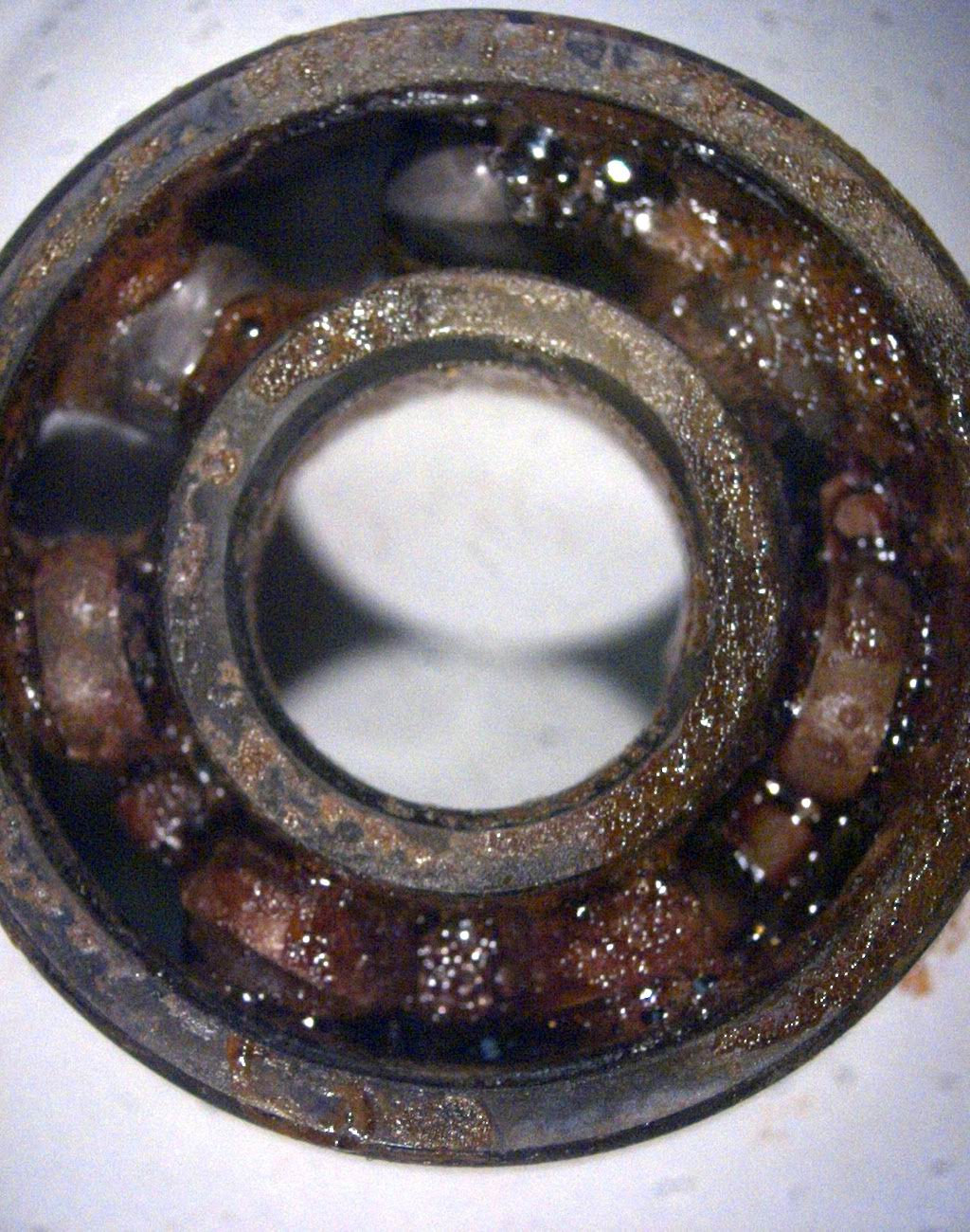
Stainless steel and chrome steel are normally corrosion-resistant, not easy to rust. However, improper storage or handling at high humidity, condensation environment will reduce bearing life. How does the corrosion of bearings happen? If the bearing is prolonged exposure to water can cause rust. With the passage of time can cause peeling and crack formation, which are premature bearing failures. In addition, if the bearing is too loose or improper installated, contact corrosion will occur.. Bearing corrosion will reduce the machine performance and productivity, increasing the cost of operation. Common raceway corrosions include, bearing contact corrosion, corrosion of the outer surface and the inner ring of holes. How to prevent bearing corrosion? Prevention is the main thing. Here are some methods which can prevent bearing corrosion 壯陽藥 Use waterproof grease, it can form a protective barrier in the wet environment Add some protective coatings, such as chrome, nickel, zinc Adjust bearing, if it is suspected of contact corrosion Try to use a different material, in extremely corrosive environment, you can use ceramic bearings for example.
The manufacturing of metal parts and components is so significant to any economic marketplace, typically, the machine tool industry is utilizing the latest technological advances in manufacturing processes. Here we’d like to talk about machine tool SPINDLE BEARING Most spindles use a combination of angular-contact ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings. The angular-contact types install at a spindle work end because they handle both axial and radial loads. The other end houses a cylindrical roller bearing which, by design, floats or slips axially to compensate for spindle thermal expansion yet operates with zero radial clearance for rigidity. The basic requirements for spindle: High running accuracy High speed Wide range of speed High rigidity Low temperature rise High reliability Some of the above requirements are in confrontation, so it’s almost impossible for spindle to meet all the above requirements simultaneously. Therefore, the main performance of spindle should be taken into consideration when designing spindle supp犀利士 orting. Bearing types and matched method depend on machine tool different performances.
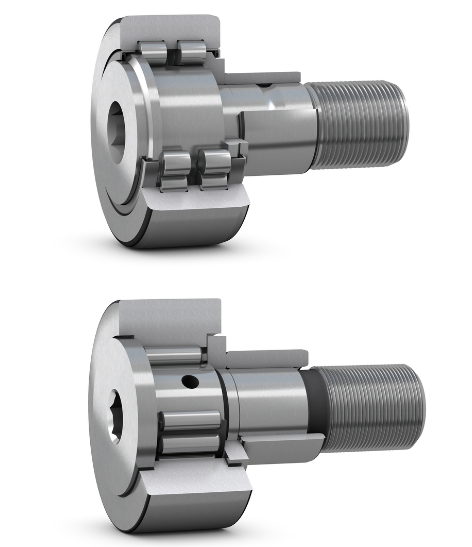
TBB Track Roller is a bearing unit composed of machined thick-wall outer ring, needle rollers or cylindrical roller sets, or cage guidance or full complement needle roller, inner ring or bolt and seal. Featuring multiple compact structure, high rotating accuracy, large varieties, broad adaptability and easy installation, it can bear high radial load and certain shock load and is widely used in machine tool, metallurgical, textile and printing machinery, processing lines and etc. Main structures as below chart: Whether you use cam follower bearings for cam followers, or for track, guide, or support rollers, their performance depends largely on the type you select. Important factors include loads, speeds, misa壯陽藥 lignment, installation, and lubrication. Cam follower bearings are used mainly in three types of applications: following the surface of a cam, supporting linear motion components, or laterally locating components during linear movement. Of these, cam follower applications range from simple two-dimensional cams to complex three-dimensional indexing cams with multiple followers… Click here for more information
Whether you use cam follower bearings for cam followers, or for track, guide, or support rollers, their performance depends largely on the type you select. Important factors include loads, speeds, misalignment, installation, and lubrication. Cam follower bearings are used mainly in three types of applications: following the surface of a cam, supporting linear motion components, or laterally locating components during linear movement. Of these, cam follower applications range from simple two-dimensional cams to complex three-dimensional indexing cams with multiple followers. Linear motion support applications include platform support rollers and die transfer rollers. Supporting a linear motion component with cam follower bearings reduces sliding friction and track wear. By reducing wear, it also helps maintain precise machine motion. Plus, cam follower bearings guide linear motion components in lateral as well as vertical directions. Basic types Cam follower types include standard stud, heavy stud, and yoke. Both stud types are mounted cantilever-style on a support housing. The heavy stud version is used for heavy loads, shock loading, or applications requiring minimal deflection. Except for the stud diameter and end plate design, standard and heavy stud versions are essentially the same. The yoke version mounts on a pin with a straddle or yoke…
Needle bearings are roller bearings with rollers that have high length-to diameter ratios. They are used in farm and construction equipment, automotive transmissions, small gasoline engines, gear pumps, small appliance and tool motors, alternators, and aircraft controls. Needle bearings are roller bearings with rollers that have high length-to diameter ratios. They are used in farm and construction equipment, automotive transmissions, small gasoline engines, gear pumps, small appliance and tool motors, alternators, and aircraft controls. Needle bearings are usually lubricated with grease, but oil or oil-mist lubrication is preferred for heavy-duty or high-speed applications. Many light-duty bearings never require relubrication, but high loads or speeds demand it. Compared with other roller bearings, needle bearings have much smaller rollers for a given bore size. They have the highest load capacity for a given radial space of all rolling-element bearings, but their use is limited to bore diameters less than 10 in. All needle bearings are variations of two basic designs. The first, full complement, has a full complement of needles and contains no retainer. The second, caged needle, contains a retainer or cage for roller guidance and spacing. Caged bearings have smaller roller complements and lower load capacities than full-complement bearings. Their…
Most rolling-element bearings are either ball or roller bearings. The roller bearing family consists basically of cylindrical, tapered, spherical, and needle bearings. Needle roller bearings are the smallest and lightest of the roller bearing family. That gives them specific advantages for certain applications, particularly those requiring reduced weight and space. The high roller length-to-diameter ratio helped give the bearings their name as well as their operating characteristics. Essentially, needle roller bearings have: • Higher load capacity than single-row ball or roller bearings of comparable OD.• The ability to handle a larger, more rigid shaft in a given application.• Excellent rolling characteristics within a small cross section.• Generally lower cost, especially for the drawn-cup type compared with machined versions. Needle rollers The most economical type of needle roller bearing is a full-complement of loose needle rollers assembled directly between a hardened and ground shaft and housing. Generally, hardened end washers provide axial location. This type appears in many applications such as those where a hardened and ground gear bore serves as the outer raceway. When application requirements are met and assembly is not difficult, a full complement of rollers forms a bearing of small cross section and high load capacity. It…