● Significance & Application of CQI-9 HTSA The North American automotive association AIAG (Automotive Industry Action Group) is the publisher of the CQI standards (Continuous Quality Improvement)….
There’s alway犀利士 s a chance that things break. Same with bearings, but it doesn’t mean that we can’t prevent those issues beforehand to avoid further troubles. The below chart will show you how beari…
Bearing in ABEC-7(P4) or ABEC-1(P0) for my application? ●What does Bearing Precision mean? When dealing with rolling bearings, precision is described by tolerance classes which include dimensiona…
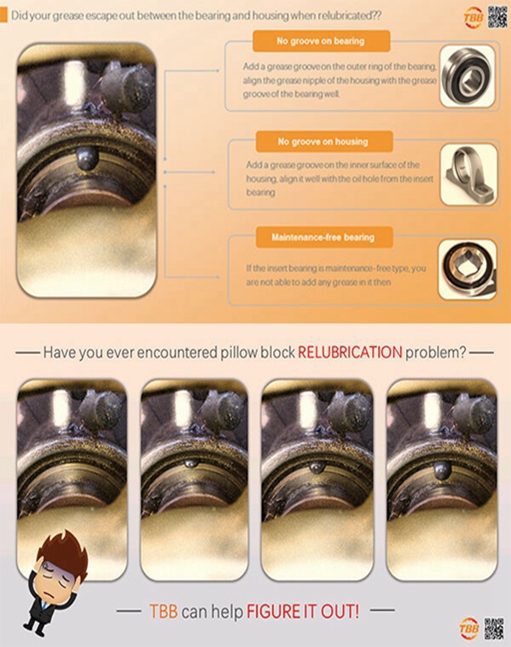
● Functions of a lubricant If rolling bearings are to operate reliably they must be adequately lubricated to prevent metal-to-metal contact between the rolling elements, raceways and cages. Separation…
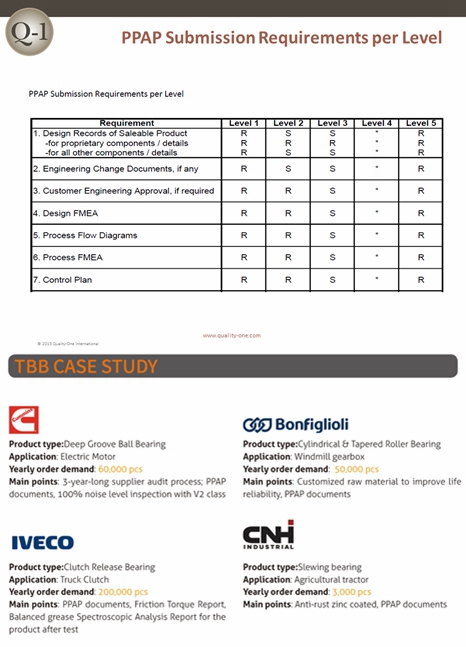
●What is PPAP? PPAP is the abbreviation of Production Part Approval Process, a valuable tool for establishing confidence in component suppliers and their production processes. Initially, PPAP was util…
Rolling element bearings are available in a variety of types, configurations, and sizes. When selecting the correct bearing for your application, it is important to take these factors below into consi…