We have assembled a wide variety of frequently asked questions (FAQs) about bearings (e.g. ball bearings, roller bearings, plain bearings, linear bearings) and bearing related products (and bearing se…
Periodic and thorough maintenance and inspection are indispensable to drawing full performance from bearings and lengthening their useful life. Besides, prevention of accidents and down time by early …
Limiting speed values for instrument bearings are almost impossible to determine. However, generalizations may be made. Bearing size: Highest speeds may be obtained with the smallest bearing. How…
Heat is generated either by shearing of the oil film or by rubbing contact. In hydrostatic and hydrodynamic bearings, heat generation at running speeds is the result of oil shear, and the amount of te…
Now we have the correct equipment for the corresponding application and now comes the turn to the installation. An incorrect installation can reduce the useful life of an equipment due to premature fa…
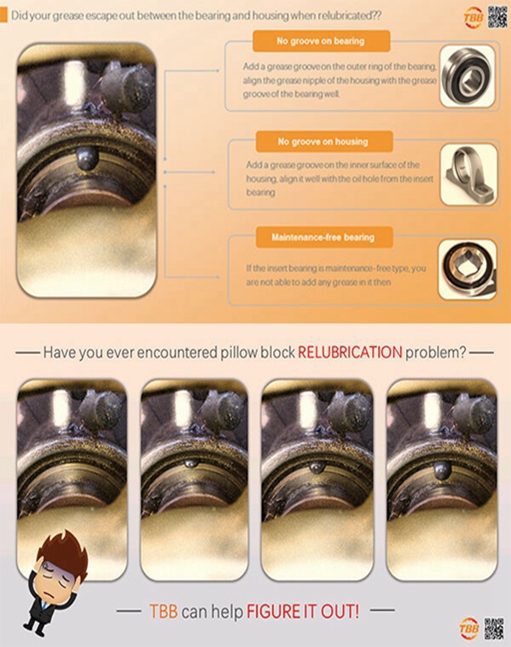
● Functions of a lubricant If rolling bearings are to operate reliably they must be adequately lubricated to prevent metal-to-metal contact between the rolling elements, raceways and cages. Separation…